Genetics and heredity crossword puzzle answer key: embark on a captivating journey into the realm of genetics and heredity, where the intricate mechanisms of inheritance unfold. This comprehensive guide unveils the fundamental principles of genetics, empowering you to solve crossword puzzles with confidence and delve deeper into the fascinating world of genetic inheritance.
Unravel the mysteries of dominant and recessive alleles, decipher the patterns of inheritance through Punnett squares, and explore the profound applications of genetics in medicine. Engage with ethical considerations that shape genetic research and testing, ensuring informed decision-making and safeguarding privacy.
Immerse yourself in the captivating world of genetics and heredity, where knowledge and curiosity intertwine to illuminate the tapestry of life.
Definition of Genetics and Heredity
Genetics is the study of heredity and variation in living organisms. Heredity refers to the passing on of traits from parents to offspring. Genetics plays a crucial role in determining the characteristics of an individual, as it governs the inheritance of physical, biochemical, and behavioral traits.
Examples of how genetics influences inherited traits include eye color, height, blood type, and susceptibility to certain diseases.
Types of Genetic Inheritance, Genetics and heredity crossword puzzle answer key
Genetic inheritance follows specific patterns, depending on the nature of the genes involved. The main types of genetic inheritance include:
- Dominant Inheritance:A dominant allele masks the expression of a recessive allele. Individuals with at least one dominant allele will exhibit the dominant trait.
- Recessive Inheritance:A recessive allele is only expressed when an individual has two copies of the allele. Individuals with one dominant and one recessive allele will not exhibit the recessive trait.
- Codominant Inheritance:Both alleles are expressed in the phenotype of individuals who have two different alleles. Neither allele is dominant or recessive.
| Inheritance Pattern | Dominant | Recessive | Codominant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allele Expression | One copy of the allele is sufficient for trait expression | Two copies of the allele are required for trait expression | Both alleles are expressed |
| Homozygous Genotype | AA | aa | BB |
| Heterozygous Genotype | Aa | Aa | AB |
| Phenotype in Homozygous Dominant | Dominant trait | Not applicable | Codominant trait |
| Phenotype in Heterozygous | Dominant trait | Not applicable | Codominant trait |
| Phenotype in Homozygous Recessive | Not applicable | Recessive trait | Not applicable |
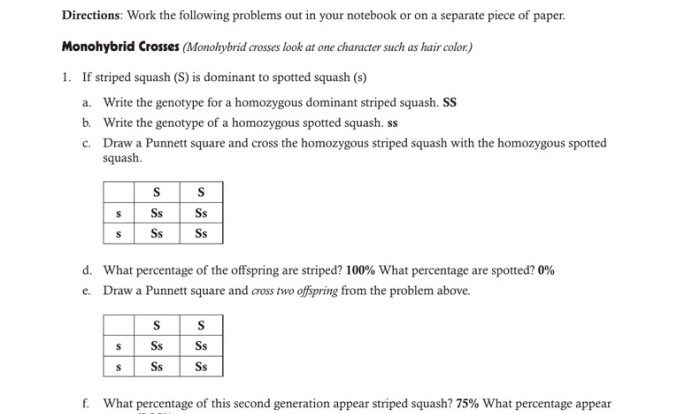
Punnett Squares and Probability
Punnett squares are used to predict the probability of inheriting specific traits. They are based on the principles of Mendelian inheritance and allow researchers to calculate the likelihood of certain genotypes and phenotypes appearing in offspring.
For example, in a Punnett square for a dominant trait, if one parent has the dominant allele (A) and the other parent has the recessive allele (a), the probability of their offspring inheriting the dominant trait is 75% (50% AA, 25% Aa).
The probability of inheriting the recessive trait is 25% (25% aa).
Applications of Genetics in Medicine
Genetics has numerous applications in medicine, including:
- Diagnosis of Genetic Disorders:Genetic testing can identify mutations or variations in genes that cause genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington’s disease.
- Treatment of Genetic Disorders:Some genetic disorders can be treated with medications or therapies that target the underlying genetic cause. For example, gene therapy can introduce functional genes into cells to correct genetic defects.
- Personalized Medicine:Genetic information can be used to tailor medical treatments and preventive measures based on an individual’s genetic profile.
Ethical Considerations in Genetics
Genetic research and testing raise important ethical issues, including:
- Informed Consent:Individuals must be fully informed about the potential risks and benefits of genetic testing before consenting to undergo it.
- Privacy:Genetic information is highly personal and should be protected from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Discrimination:Genetic information could potentially be used to discriminate against individuals based on their genetic predispositions or carrier status.
Common Queries: Genetics And Heredity Crossword Puzzle Answer Key
What is the difference between dominant and recessive alleles?
Dominant alleles express their trait even when paired with a recessive allele, while recessive alleles only express their trait when paired with another recessive allele.
How can Punnett squares be used to predict the probability of inheriting specific traits?
Punnett squares are a visual tool used to determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents.
What are some ethical considerations related to genetic research and testing?
Ethical considerations include informed consent, privacy, and the potential for genetic discrimination.